Table of Contents
- Understanding the Importance of a Security Audit
- Pre-Audit Preparation: Setting Your Objectives
- Assembling Your Security Audit Team
- Identifying Key Assets and Data Systems
- Creating a Comprehensive Audit Checklist
- Gathering and Analyzing Security Policies
- Evaluating Physical Security Measures
- Assessing Network Security
- Performing Vulnerability Scanning
- Conducting Penetration Testing
- Formulating an Action Plan for Mitigation
- What tools are recommended for performing a security audit
- How The Use Of A Virtual Data Room Can Help With More Secure Data Management
Understanding the Importance of a Security Audit
Security audits are an indispensable part of an organization’s overall strategy for safeguarding its IT systems and data. By conducting these audits, companies of all sizes can proactively identify weaknesses and areas vulnerable to potential threats. This evaluation serves not only to protect sensitive customer information through encryption and access controls but also to fortify trust and maintain a strong reputation.
Another point to consider is that organizations must wrestle with cyberattacks, new vulnerabilities, and security threats in remote and hybrid working arrangements.
Security audits support compliance with regulatory requirements and help in the development of robust risk assessment and mitigation plans. Conducting regular audits ensures that your organization remains vigilant and responsive to new security challenges.
Pre-Audit Preparation: Setting Your Objectives
Before diving into the audit itself, it’s crucial to clearly define what you aim to achieve. Streamlining your objectives will help guide the entire audit process and ensure that energy and resources are efficiently utilized. Start by asking key questions about your organizational goals—
Are you aiming to comply with specific regulations?
Do you need to bolster your overall security framework?
By clarifying the end goals, you ensure everyone is aligned, which helps prevent scope creep and keeps the audit focused and relevant.
Next, gather all necessary documents and information that will be essential during the audit. This could include previous audit reports, network diagrams, cybersecurity policies, and lists of hardware and software assets. Having this data on hand can expedite the process and provide a comprehensive view of your security landscape.
Coordination with key stakeholders is another pivotal aspect. Whether it’s the IT department, compliance teams, or executive leadership, getting their buy-in and understanding their priorities will help tailor the audit objectives to align with broader business strategies. Make sure you have a clear communication plan in place to keep everyone informed throughout the process.
Finally, establish a timeline for the audit. Break the process down into manageable phases with clear deadlines to ensure that every step is carried out meticulously. A well-structured timeline mitigates the risk of rushed assessments, which can lead to missed vulnerabilities.
Assembling Your Security Audit Team
An effective security audit begins with selecting the right professionals for the job. Both internal and external auditors bring unique perspectives that can enhance the audit’s comprehensiveness. Internal auditors have an in-depth understanding of the existing systems and procedures, while external auditors offer an unbiased viewpoint and can identify blind spots that might be overlooked by in-house teams.
Start by identifying key team members who possess a comprehensive understanding of cybersecurity policies, information systems, and current threats. Your team should include individuals with skills in network security, data protection, compliance, and risk management. Additionally, consider involving employees who routinely handle sensitive data or manage critical systems, as they can provide valuable insights during the assessment.
It’s important to define clear roles and responsibilities for each team member. For instance, you might designate a lead auditor to oversee the process, analysts to review logs and reports, and interviewers to gather information from employees. Establishing an organized structure ensures that every aspect of your security audit is covered systematically.
Encourage open communication among team members to foster collaboration. Regular meetings and status updates can help synchronize efforts and address any emerging challenges promptly. Provide access to essential resources such as security policies, system diagrams, and incident reports. Equipping your team with the right tools and information is crucial for a thorough and effective audit.
Identifying Key Assets and Data Systems
Identifying your key assets and data systems is a foundational step in any security audit. Consider these assets as the crown jewels of your organization—anything that, if compromised, could disrupt your operations or leak sensitive information. Common examples include customer databases, financial records, intellectual property, and critical IT infrastructure such as servers, networks, and software applications.
Start by cataloging these assets. Create a detailed inventory that lists each asset, its location, and its current security measures. This inventory should be comprehensive, covering both physical and digital assets. Include everything from the hardware in your data centers to cloud services and software applications your team uses daily.
Once you have your inventory, prioritize your assets based on their importance and the potential impact of a security breach. Engage with stakeholders to understand which data systems are considered most sensitive and mission-critical. This collaborative approach ensures that you’re aligned with business priorities and enables you to focus your audit efforts where they’re needed most.
Next, map out the data flow and interconnections between these assets. Understanding how data moves within your organization and where it resides at various points can help you identify vulnerabilities. For example, are there unsecured transfer protocols? Are third-party vendors accessing your data? Knowing these details can point out areas requiring stringent security controls.
In addition to digital assets, don’t forget to consider physical access points. Evaluate how your organization controls physical access to information assets and IT services. Are there robust access control systems in place? Is there surveillance to deter unauthorized entry? All these physical security measures are crucial for protecting your data systems.
Finally, document the existing security controls for each asset. This includes encryption protocols, firewall settings, access permissions, and any monitoring systems already in place. Having this record not only helps in identifying gaps but also provides a benchmark against which you can measure improvements post-audit.
Creating a Comprehensive Audit Checklist
Once you’ve identified your key assets and data systems, it’s crucial to establish an exhaustive audit checklist. This checklist serves as your roadmap to ensure no aspect of your security posture is overlooked. Tailoring this checklist to match your organization’s unique infrastructure and compliance requirements will maximize its effectiveness. Below are some critical components that should be included:
- IT Infrastructure: Assess your network setup, hardware, software applications, and cloud services. Ensure all systems are updated and configured correctly.
- Sensitive Data Storage: Examine how sensitive data is stored, transmitted, and accessed. Verify the encryption methods and access control mechanisms in place.
- Physical Security Practices: Review the physical security of your premises, including access points, surveillance systems, and visitor management protocols.
- Cybersecurity Policies and Procedures: Audit existing cybersecurity policies to ensure they are comprehensive and up-to-date. Evaluate the effectiveness of incident response plans, employee training programs, and regular security updates.
- Compliance Standards: Confirm that your organization’s operations align with relevant regulatory requirements and industry standards. This includes GDPR, HIPAA, ISO/IEC 27001, and other applicable frameworks.
Establishing robust criteria for each item on your checklist helps ensure a systematic and thorough audit. Remember, a comprehensive checklist is a living document that should be continuously updated to reflect new threats, technologies, and regulatory changes. Properly maintained, it will be an invaluable tool for safeguarding your organization’s data management systems.
For a more comprehensive checklist download our “Security Audit Full Checklist” here
Gathering and Analyzing Security Policies
Understanding your current security policies is a critical step. Begin by collecting all internal policies related to cybersecurity. These policies often spell out the rules and procedures for safeguarding your data and can provide a roadmap for your audit.
But why focus on policies? Well, policies play a key role in thwarting specific cybersecurity threats. By dissecting these documents, you can identify gaps and weaknesses in your organization’s defense mechanisms.
The next step involves careful analysis. Cross-reference your policies with industry standards and best practices. This comparison will help you evaluate the effectiveness of your current security measures. Are your policies up-to-date? Do they cover new and emerging threats? This phase is all about identifying areas that need improvement to ensure that your security posture is robust and compliant with industry norms.
Centralizing your cybersecurity, risk management, and compliance policies into a single document can greatly simplify the audit process. This consolidated document acts as a comprehensive reference that can speed up the audit, making it easier to spot inconsistencies and areas that require attention.
Interviews with key stakeholders are also invaluable during this stage. They can offer insights into how policies are enforced, understood, and adhered to across the organization. These conversations shed light on the effectiveness of your security controls and the practical challenges that might not be apparent from a policy document alone.
In summary, gathering and analyzing your security policies is a foundational step in your audit process, setting the stage for a thorough evaluation of your security infrastructure.
Evaluating Physical Security Measures
Evaluating physical security measures means ensuring that all physical barriers and access controls are effectively safeguarding your assets. Start by checking that all entry points—doors, windows, gates—are secure and that proper locking mechanisms are in place. Evaluate the effectiveness of perimeter defenses like fences and security guards, and ensure that surveillance cameras are strategically placed to cover vulnerable areas.
Next, assess the security of critical areas like server rooms and data centers. Access to these zones should be restricted and monitored. Implement key card systems, biometric scanners, or other advanced entry controls to limit access to authorized personnel only. Don’t forget about monitoring and logging entries and exits for audit purposes.
Another essential step is to review your environmental controls. Make sure fire suppression systems, climate controls, and backup generators are in good working order. These systems play a crucial role in protecting physical hardware from environmental threats.
Lastly, don’t overlook the importance of training your staff. Ensure they are familiar with physical security protocols and understand their role in maintaining security. Regular drills and updates can help keep everyone prepared for potential security incidents.
Assessing Network Security
Your network is the backbone of your IT infrastructure, making it a prime target for cyber threats. To safeguard it, a meticulous evaluation is necessary.
Start by identifying all network components, including routers, switches, firewalls, and wireless access points. Document their configuration and ensure each one adheres to your organization’s security policies.
Firewall Rules: Review and update firewall rules to restrict unauthorized access while allowing legitimate traffic. Pay special attention to inbound and outbound traffic policies.
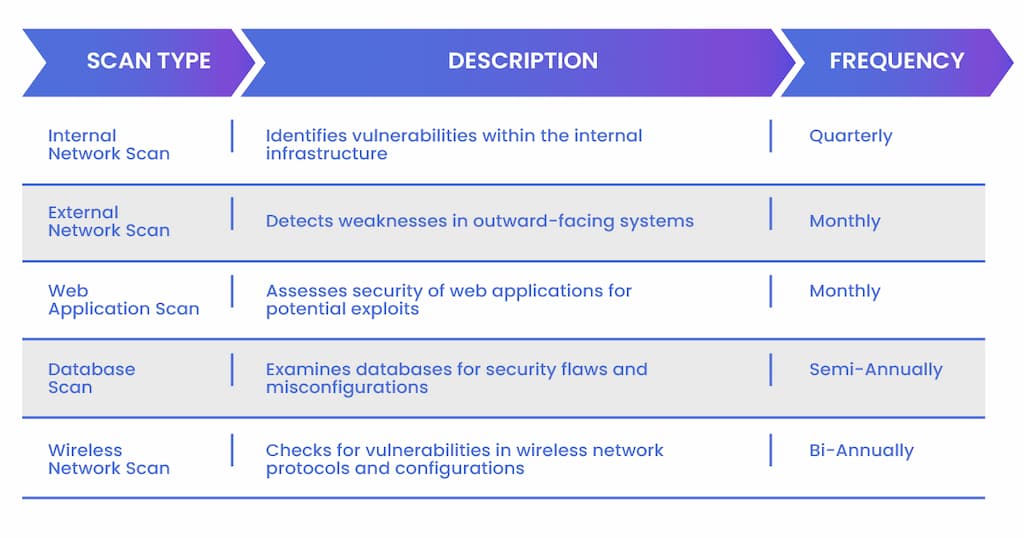
Vulnerability Scanning: Utilize advanced tools to perform regular vulnerability scans. Scanning helps detect potential entry points that cybercriminals might exploit. Address any discovered issues promptly.
Next, examine Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS). Affording real-time monitoring and quick response to threats, an IDS/IPS should be calibrated to recognize and mitigate suspicious activities.
Additionally, verify all access control measures across the network. Ensure role-based access and enforce the principle of least privilege. This minimizes the risk of unauthorized access by limiting user permissions to only what’s necessary for their role.
Don’t ignore the importance of network segmentation. Dividing your network into separate segments can significantly limit the spread of malware and other threats, should an incident occur.
Encryption: Implement encryption protocols for data in transit across your network. Technologies like VPNs and HTTPS ensure that sensitive information remains secure from eavesdropping.
Finally, keep your network devices and software consistently updated with the latest security patches. Regular updates fix known vulnerabilities, closing the door to many potential attacks.
Performing Vulnerability Scanning
Vulnerability scanning is a critical component of any security audit. This process involves using automated tools to inspect your systems for known vulnerabilities, such as unpatched software, insecure configurations, and open ports.
Start by selecting the appropriate vulnerability scanning tools for your needs. Popular options include Nessus, OpenVAS, and Qualys. These tools can provide you with detailed reports on potential security weaknesses. Ensure these tools are up-to-date to recognize the latest vulnerabilities.
Once your tools are ready, it’s time to configure and run the scans. Set the parameters to cover all relevant parts of your network and systems. It’s essential to include both internal networks and externally facing systems to get a comprehensive view of your security posture.
After running the scans, you’ll receive reports highlighting detected vulnerabilities. These reports typically categorize vulnerabilities by severity, making it easier to prioritize remediation efforts. Pay close attention to high and critical severity vulnerabilities, as these pose the greatest risk to your organization.
Next, analyze the scan results with your audit team. This collaborative step ensures that you understand the implications of each vulnerability and develop a prioritized action plan to address them. It may also involve verifying the findings manually in some cases.
Finally, document your findings and remediation plans. This documentation is crucial for tracking your progress over time and demonstrating compliance with regulatory requirements. Regularly scheduled vulnerability scans should become a part of your continued security practice to maintain a robust security posture.
Conducting Penetration Testing
Penetration testing, often referred to as “pen testing,” is a simulated cyber attack aimed at evaluating the security of your system. This involves utilizing both automated tools and manual techniques to identify vulnerabilities that could potentially be exploited by malicious actors. While penetration tests may sound intimidating, they are indispensable in uncovering weaknesses that standard security audits might overlook.
Begin by defining the scope of your penetration test. This includes deciding which systems or networks will be tested, setting clear objectives, and outlining any constraints. The scope should be as comprehensive as possible to ensure no critical areas are left unexamined.
Next, select a reputable penetration testing provider or use in-house experts if available. Skilled testers will employ a variety of techniques such as exploiting software bugs, configuration errors, and design flaws. They will also attempt to bypass security controls to gain unauthorized access, providing practical insights into potential threats.
During the pen test, the team will document their findings in detail. These reports usually cover discovered vulnerabilities, the methods used to exploit them, and the potential impact on your organization. This documentation is vital for understanding the context of each vulnerability and serves as a roadmap for remediation efforts.
Post-pentest, gather your audit team to review the findings. Prioritize vulnerabilities based on their severity and the likelihood of exploitation. Develop an action plan to address these issues, which may involve applying patches, enhancing configurations, or revising security policies. Remember, a successful penetration test is not just about identifying vulnerabilities; it’s about taking proactive steps to mitigate them.
Finally, consider making penetration testing a regular part of your security strategy. Threat landscapes evolve, and new vulnerabilities emerge constantly. Regular testing ensures that your defenses keep pace with potential threats, providing peace of mind and enhancing overall security posture.
Formulating an Action Plan for Mitigation
Once you’ve conducted the vulnerability scanning and penetration testing, your next step is to distill your findings into a detailed action plan. This plan will be your roadmap to fortifying your security posture and ensuring your organization is well-protected against threats.
Begin by prioritizing risks. Not all vulnerabilities are created equal, and it’s crucial to address the most critical threats first. Categorize them based on factors such as potential impact, the probability of exploitation, and the value of the affected asset.
After prioritizing, outline the remediation steps for each identified risk. This could range from applying software patches, reconfiguring network settings, to more extensive measures like overhauling entire systems. Ensure these steps are practical and feasible within your current resources and timeline.
A well-rounded action plan also includes a business continuity plan (BCP) and a disaster recovery plan (DRP). The BCP should detail how your organization will continue functioning during and after any security incidents, while the DRP focuses on restoring your IT systems and data to full operation. Consider factors such as alternate work locations, data backups, and safeguard procedures.
Don’t forget to document your prevention tools and strategies. This includes firewalls, anti-malware programs, intrusion detection systems, and any other security technologies you employ. Proper documentation ensures that everyone is aware of the tools at their disposal and how to use them effectively.
Integrating a communication plan is another essential component. Clearly outline how incidents should be reported and who needs to be notified. This ensures timely and coherent communication during a crisis, minimizing confusion and delays.
Lastly, invest in employee training. Even the best security technologies can be rendered ineffective if your staff isn’t aware of the threats and how to handle them. Regular training sessions, workshops, and simulated phishing attacks can significantly enhance your team’s responsiveness to security incidents.
What tools are recommended for performing a security audit?
When it comes to conducting a security audit, having the right tools can make all the difference. Here are some of the most recommended tools for performing a thorough security audit:
- Nmap: This open-source tool is widely used for network discovery and security auditing. It helps you map your network, providing insights into hosts, services, operating systems, and potential vulnerabilities.
- Wireshark: Another open-source tool, Wireshark is essential for network protocol analysis. It allows you to capture and interactively browse the traffic running on a computer network, helping to identify suspicious activity.
- Nessus: Offered by Tenable, Nessus is a vulnerability scanner that helps identify vulnerabilities across various platforms. It’s known for its comprehensive scanning capabilities and detailed reporting.
- OWASP ZAP: The OWASP Zed Attack Proxy (ZAP) is designed for finding security vulnerabilities in web applications. It’s user-friendly and efficient for both developers and testers.
- Burp Suite: Widely used by security professionals, Burp Suite offers a range of tools for testing web application security. It includes features for scanning, crawling, and analyzing the security of web applications.
- Metasploit: A powerful penetration testing framework, Metasploit allows you to find, exploit, and validate vulnerabilities. It’s comprehensive and constantly updated with the latest exploits.
- SolarWinds Security Event Manager: This tool provides real-time log analysis, security monitoring, and helps with compliance. It’s particularly useful for auditing and keeping track of security events.
- QualysGuard: A cloud-based platform, QualysGuard offers tools for vulnerability management, policy compliance, and web application scanning. It’s scalable and user-friendly, suitable for organizations of any size.
How The Use Of A Virtual Data Room Can Help With More Secure Data Management
Utilizing a Virtual Data Room (VDR) can significantly enhance the security of your data management systems, particularly during a security audit. Unlike traditional data storage solutions, a VDR provides a secure, centralized repository that is designed to facilitate better control over sensitive information.
- Enhanced Security Features: VDRs come equipped with advanced encryption, multi-factor authentication, and intricate permission settings. These features ensure that only authorized personnel can access specific data, thereby reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Real-time Audit Logs: A VDR maintains comprehensive, real-time audit trails of all data interactions. This allows audit teams to track who accessed what data and when, offering a clearer view of any potential security incidents. This transparency is invaluable for compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR.
- Streamlined Collaboration: With a VDR, your audit team can seamlessly collaborate on identifying and addressing vulnerabilities. The centralized platform makes it easier to manage documents, share insights, and coordinate activities without compromising security.
- Simplified Compliance: By centralizing your cybersecurity, risk management, and compliance policies in a VDR, you facilitate easier audits and quicker responses to regulatory changes. VDRs can help track updates and ensure that your security measures evolve in line with new compliance requirements.
- Cost-Efficiency: Reducing the need for physical storage and minimizing the risk of data breaches can lower overall costs. The added layer of protection that VDRs provide ensures that investments in security yield long-term savings.
Incorporating a VDR into your security audit process not only strengthens your data protection measures but also enhances the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the audit itself. By leveraging these advanced features, you can build a more resilient defense against potential threats, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of your sensitive information.