As we approach 2025, the cybersecurity landscape continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace, shaped by the increasing sophistication of cyber attackers and the rapid expansion of digital infrastructures. The past year alone has seen significant shifts in the methods and magnitude of cyber threats, making it clear that staying vigilant and informed is more crucial than ever.
Understanding and anticipating emerging threats is not merely a matter of safeguarding information; it is essential for maintaining the integrity of our digital ecosystems and the trust of the stakeholders involved. This report delves into the future of cybersecurity threats, providing a forward-looking analysis aimed at preparing organizations for what lies ahead.
In crafting this report, we have drawn from a diverse range of data sources, including threat intelligence feeds, recent cybersecurity conferences, expert panel discussions, and a review of recent high-profile cyber incidents. Our methodology combines qualitative insights from leading security experts with quantitative data from trusted cybersecurity firms to provide a summary overview of the threats that are poised to shape 2025.
By examining these trends and preparing accordingly, businesses and individuals can not only defend against, but also get ahead of, the cybersecurity challenges on the horizon.
Table of Contents
- The Evolution of Ransomware
- Deepfake Technology and Its Implications
- IoT and Smart Device Vulnerabilities
- Supply Chain Attacks: A Growing Concern
- AI-Driven Cyber Attacks
- Cloud Security Challenges
- The Role of 5G in Cybersecurity
- Regulatory and Compliance Changes
- Conclusion: Navigating the Future of Cybersecurity and the Role of Virtual Data Rooms in 2025
1. The Evolution of Ransomware
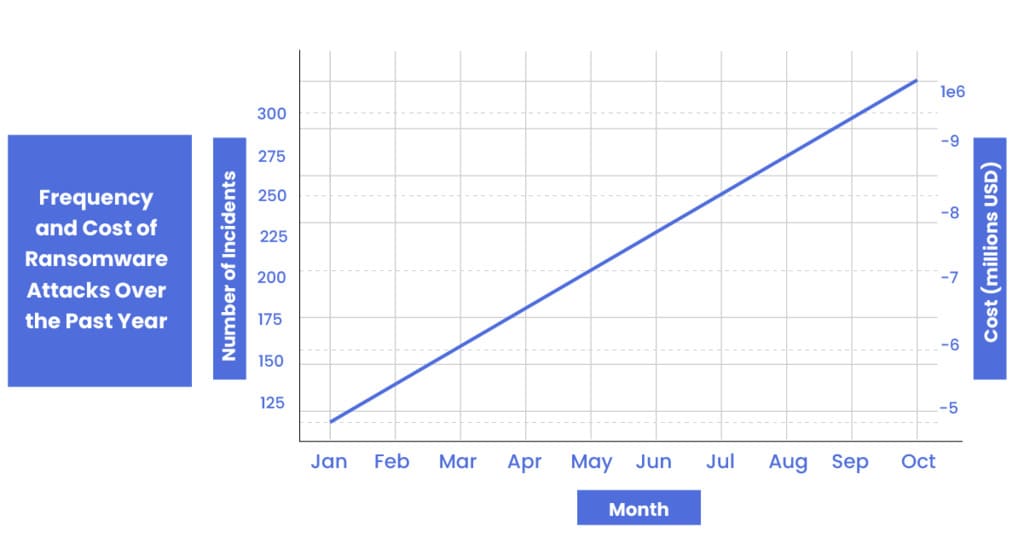
Ransomware remains one of the most pervasive and damaging types of cyber threats faced by organizations globally. In recent years, the sophistication and frequency of ransomware attacks have escalated, compelling both public and private sector entities to rethink their defense strategies.
This section explores the recent trends, provides forecasts for the evolution of ransomware tactics in 2025, and examines case studies of notable incidents.
- Recent Trends in Ransomware Attacks:
- Increased Targeting of Critical Infrastructure: Attacks on healthcare, energy, and municipal services have shown that cybercriminals are focusing on high-value targets with the potential to cause widespread disruption.
- Rise of Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS): Cybercriminal groups are selling or renting ransomware capabilities to other criminals, broadening the scope of attackers.
- Double Extortion Tactics: More attackers are not just encrypting data but also threatening to release it publicly if the ransom isn’t paid, adding pressure on victims to comply.
- Predictions for 2025:
- Greater Use of AI in Attacks: As artificial intelligence tools become more refined, they will likely be used to customize ransomware attacks based on automatic detection of system vulnerabilities.
- Exploitation of Emerging Technologies: With the expansion of 5G and IoT, ransomware could increasingly target these technologies to exploit new vulnerabilities.
- Increased Attacks During Significant Global Events: Cybercriminals may capitalize on events like elections, major sports events, or global summits to launch ransomware attacks when organizations are most vulnerable.
- Case Studies of Recent High-Profile Ransomware Incidents:
- Case Study 1: Healthcare Sector Attack
- Victim: A major hospital chain.
- Impact: Disruption of patient care services, cancellation of surgeries, leakage of sensitive patient data.
- Outcome: The hospital paid a substantial ransom to restore access and prevent data leakage.
- Case Study 2: Energy Sector Attack
- Victim: A national electricity supplier.
- Impact: Widespread power outages, significant operational disruption.
- Outcome: The attack triggered a federal response, highlighting the national security implications of ransomware.
- Case Study 1: Healthcare Sector Attack
This analysis underscores the critical need for enhanced cybersecurity measures and the development of rapid response strategies to combat the evolving threat of ransomware effectively in 2025.
2. Deepfake Technology and Its Implications
“Deepfakes can do incredible damage to reputations and the truth.”
Danielle Citron, Law Professor at the University of Virginia and author of “Hate Crimes in Cyberspace”
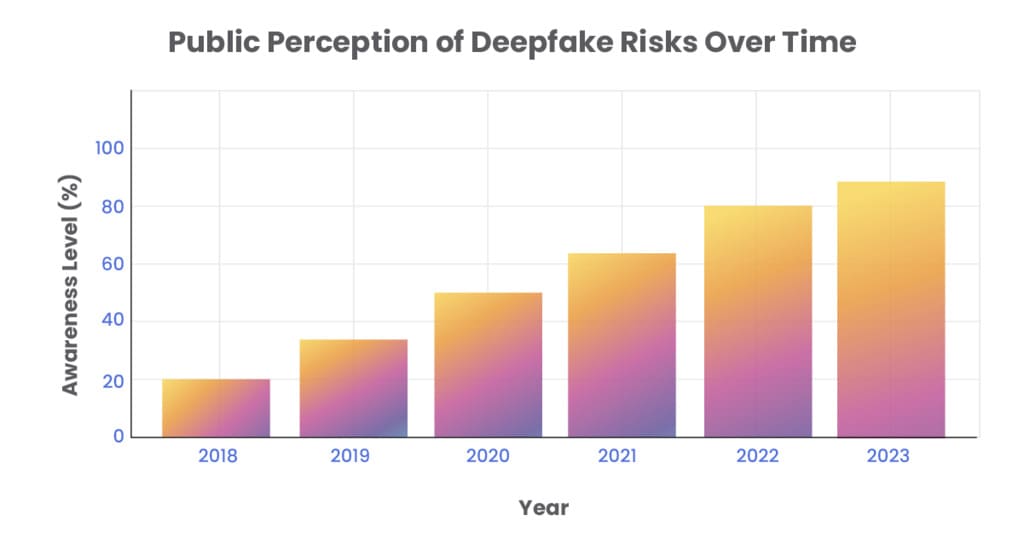
Deepfake technology, a product of artificial intelligence and machine learning, enables the creation of convincingly realistic video and audio recordings where the appearance and voice of one person can be swapped with another. As this technology advances, it presents increasingly complex challenges for cybersecurity.
- Explanation of Deepfake Technology:
- How It Works: Deepfakes are created using generative adversarial networks (GANs), where two machine learning models work against each other; one creates the fake images or videos, and the other attempts to detect the fakes. Over time, the generator becomes adept at producing highly convincing fakes.
- Accessibility: Advances in software tools have made this technology more accessible to the general public, not just expert programmers.
- Potential Risks Associated with Deepfakes in Cybersecurity:
- Misinformation: The ability to create realistic fake videos can lead to widespread misinformation, potentially influencing public opinion and political processes.
- Identity Theft: Impersonation of individuals in videos can lead to identity theft, damaging reputations and causing personal and professional harm.
- Fraud and Scams: Deepfakes can facilitate convincing scams by mimicking voices or faces of trusted individuals, tricking victims into transferring money or revealing sensitive information.
- Real-world Examples of Deepfake Incidents Affecting Security:
- Politics: A well-known politician was falsely depicted in a video giving inflammatory remarks, which briefly stirred international tensions.
- Corporate Espionage: A CEO’s deepfake was used to give fraudulent instructions for financial transactions, leading to significant financial losses for the company.
- Legal and Ethical Dilemmas: Legal systems struggle to keep pace with the technology, complicating the prosecution of crimes involving deepfakes.
Understanding and mitigating the risks associated with deepfake technology is crucial for maintaining security integrity in an era where seeing and hearing can no longer be believing. As these tools become more sophisticated and widespread, proactive measures and regulations will be essential to combat the associated threats.
3. IoT and Smart Device Vulnerabilities
The proliferation of the Internet of Things (IoT) devices in both residential and industrial settings has transformed everyday life and operational efficiencies. However, this rapid expansion also brings with it an array of cybersecurity vulnerabilities. This section discusses the growth trends of IoT devices, identifies common security weaknesses, and provides actionable steps to mitigate these risks.
- Growth of IoT Devices in Home and Industrial Settings:
- Residential Growth: Smart home devices such as thermostats, cameras, and home assistants have seen exponential growth, integrating more aspects of home life into the digital sphere.
- Industrial Adoption: In industrial settings, IoT devices are crucial for monitoring, automating processes, and improving efficiency in sectors like manufacturing, logistics, and agriculture.
- Common Vulnerabilities Found in IoT Devices:
- Insecure Interfaces: Many IoT devices have weak authentication and open network ports, making them easy targets for cyber attacks.
- Lack of Regular Updates: IoT devices often lack the capability or the policy framework for regular firmware updates, leaving known vulnerabilities unpatched.
- Data Privacy Issues: IoT devices collect vast amounts of personal data, which is not always securely stored or transmitted, leading to privacy concerns.
- Steps for Mitigating Risks Associated with IoT Security:
- Secure Configuration: Default configurations should be altered to strengthen security settings and disable unnecessary services.
- Regular Updates: Implement policies to regularly update and patch IoT devices to protect against known threats.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate IoT devices on separate network segments to limit the spread of potential intrusions.
- Enhanced Authentication: Use strong, unique passwords and consider multi-factor authentication to enhance security.
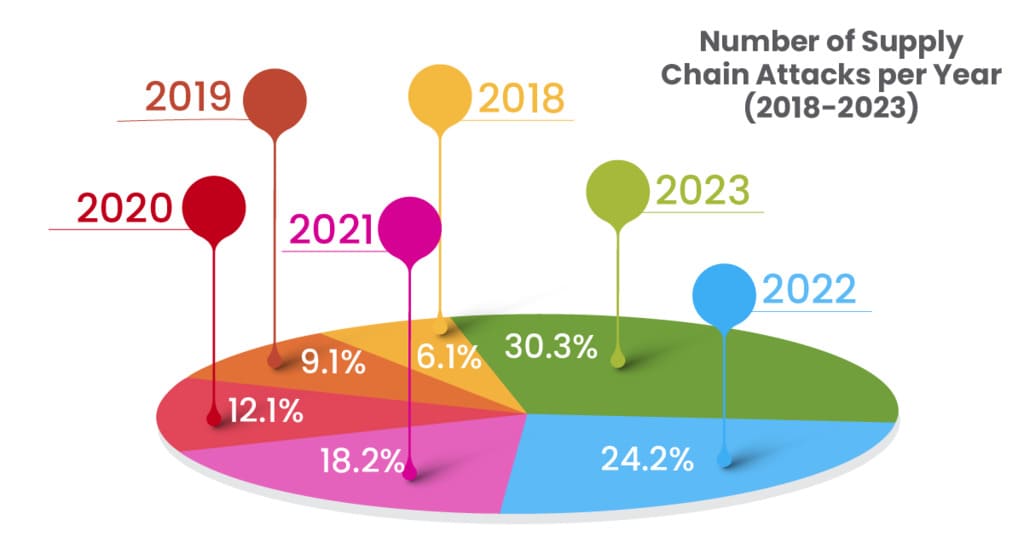
4. Supply Chain Attacks: A Growing Concern
Supply chain attacks target multiple organizations through a single, often less-secured, point in the supply chain. As dependencies between suppliers and clients grow, so does the vulnerability to such attacks.
- Understanding Supply Chain Attacks:
- Dependency Weaknesses: Attackers exploit vulnerabilities in a single supplier to compromise all its clients.
- Recent Upticks in Attacks: An increase in remote work and digital collaboration tools has expanded the attack surface.
- Mitigating Supply Chain Risks:
- Due Diligence: Regular security assessments of suppliers.
- Incident Response Plans: Coordinated response strategies among all parties in the supply chain.
- Continuous Monitoring: Real-time monitoring of activities across the supply chain to detect and respond to threats promptly.
5. AI-Driven Cyber Attacks
Artificial intelligence is becoming a tool for both defenders and attackers in the cybersecurity arena. AI-driven attacks can be particularly dangerous due to their speed and evolving nature.
- The Rise of AI in Cybersecurity:
- Automated Attacks: AI can conduct attacks at scale, quickly finding and exploiting vulnerabilities.
- Adaptive Threats: AI systems can learn and adapt from each interaction, making them increasingly effective over time.
- Defending Against AI Attacks:
- Advanced Detection Systems: Utilize AI-powered systems to detect unusual patterns that may indicate AI-driven threats.
- Regular Training and Updates: Keeping security teams well-trained on the latest AI threats and countermeasures.
- Collaborative Defense Strategies: Sharing information on AI threats with other organizations to improve collective security.
6. Cloud Security Challenges
“When you move services to the cloud, you are transferring a huge part of your responsibility to the security of that data to someone else.”
Kevin Mitnick, World-renowned Cybersecurity Expert and Hacker
As more organizations migrate to cloud-based services, the complexity of cloud security continues to increase.
- Expansion of Cloud Usage:
- Diverse Platforms: Adoption of various cloud services (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) introduces multiple points of vulnerability.
- Integration Issues: Challenges in integrating legacy systems with cloud services can create security gaps.
- Cloud Security Best Practices:
- Data Encryption: Encrypt data both in transit and at rest.
- Access Controls: Implement stringent access controls and identity verification processes.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct audits to ensure compliance with security policies and to identify potential vulnerabilities.
7. The Role of 5G in Cybersecurity
“With 5G, the security landscape will become more complex and, at the same time, more critical than ever.”
Boris Wojtan, Director of Privacy at GSMA
The deployment of 5G technology is set to revolutionize communication but also introduces new cybersecurity challenges.
- 5G and New Vulnerabilities:
- Increased Attack Surface: More devices and faster speeds increase the potential for cyber attacks.
- Edge Computing Risks: Shifting data processing to the edge can expose vulnerabilities in less secure areas.
- Securing 5G Networks:
- Enhanced Encryption Techniques: Leveraging stronger encryption standards to protect data.
- Network Slicing: Using network slicing to isolate and protect sensitive information and operations.
- Advanced Intrusion Detection Systems: Deploying state-of-the-art detection systems tailored for the high-speed environment of 5G networks.
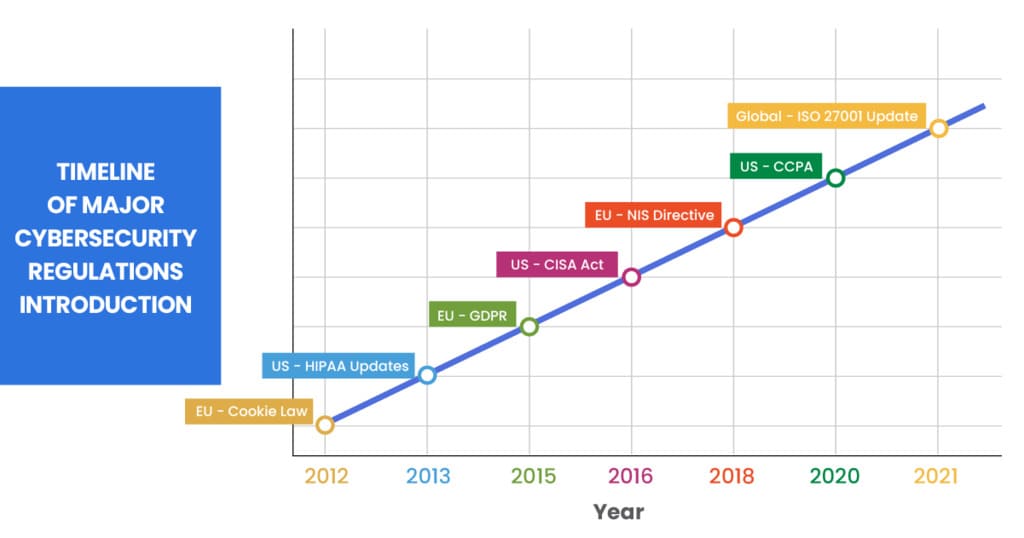
8. Regulatory and Compliance Changes
Staying compliant with cybersecurity regulations is not only a legal requirement but also a critical component of an effective security strategy.
- Upcoming Regulatory Changes:
- Global Data Protection Regulations: An overview of new and upcoming regulations, such as updates to GDPR or new legislation in other countries.
- Sector-Specific Regulations: Changes targeting specific industries, like healthcare and finance.
- Strategies for Compliance:
- Compliance Teams: Establish specialized teams to focus on compliance issues.
- Continuous Training: Regular training for all employees on compliance requirements and best practices.
- Compliance Software Solutions: Implementing and utilizing software that helps maintain compliance with various regulations.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of Cybersecurity and the Role of Virtual Data Rooms in 2025
As we have explored the various facets of the evolving cybersecurity landscape for 2025, from the perils of deepfake technology and IoT vulnerabilities to the complexities of cloud security and the explosive potential of 5G networks, it’s clear that the digital threats organizations face are becoming increasingly sophisticated and interconnected.
The implications of these threats underscore the necessity for robust, forward-thinking cybersecurity strategies that not only address current challenges but are also adaptable to future risks.
In this context, the role of Virtual Data Rooms (VDRs) becomes more critical than ever. VDRs are designed to offer secure online spaces where sensitive information, such as financial documents, intellectual property, and legal contracts, can be stored and shared with confidence. As cyber threats proliferate, the capabilities of VDRs must evolve to meet these challenges:
- Enhanced Security Features: By 2025, it is expected that VDRs will incorporate advanced encryption methods, multi-factor authentication, and AI-driven security protocols to detect and neutralize threats in real-time.
- Regulatory Compliance: With the anticipated updates to global data protection regulations, VDRs will need to ensure compliance through features that can adapt to the diverse legal landscapes, helping organizations navigate the complexities of data sovereignty and privacy laws.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: As businesses increasingly adopt IoT, 5G, and cloud services, VDRs will need to seamlessly integrate with these technologies, providing a secure bridge that manages and protects data across various platforms.
The strategic use of VDRs in mitigating supply chain risks and supporting secure transactions in an increasingly interconnected world highlights their importance. They serve not only as a tool for data protection but also as a facilitator of safe, efficient collaboration across distances and industries.
Ultimately, as we look toward 2025, the integration of sophisticated cybersecurity measures into every aspect of digital engagement will be paramount. Virtual Data Rooms like ShareVault, with their focus on security and compliance, will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in ensuring that businesses can share, collaborate, and innovate without compromising on security.
As cyber threats evolve, so too must our defenses, with VDRs standing on the front lines of the effort to secure our digital futures.