In today’s digital age, where information is at the heart of business operations, maintaining data security and confidentiality has become a paramount concern for organizations across industries. As businesses increasingly rely on sharing sensitive information with partners, investors, and other stakeholders, the need for secure and confidential data exchange has grown exponentially. In response to this demand, a virtual data room (VDR) has emerged as a powerful tool that not only facilitates the secure sharing of sensitive data but also ensures robust data security and confidentiality.
What is a Virtual Data Room?
A virtual data room is an online repository used for securely storing and sharing sensitive documents and information. Originally, virtual data rooms found their roots in the financial and legal sectors, where due diligence processes, mergers and acquisitions, fundraising, and regulatory compliance required the exchange of confidential documents among multiple parties.
However, their utility has expanded to various industries where secure information sharing is crucial, including therapeutics, real estate, energy, and more.
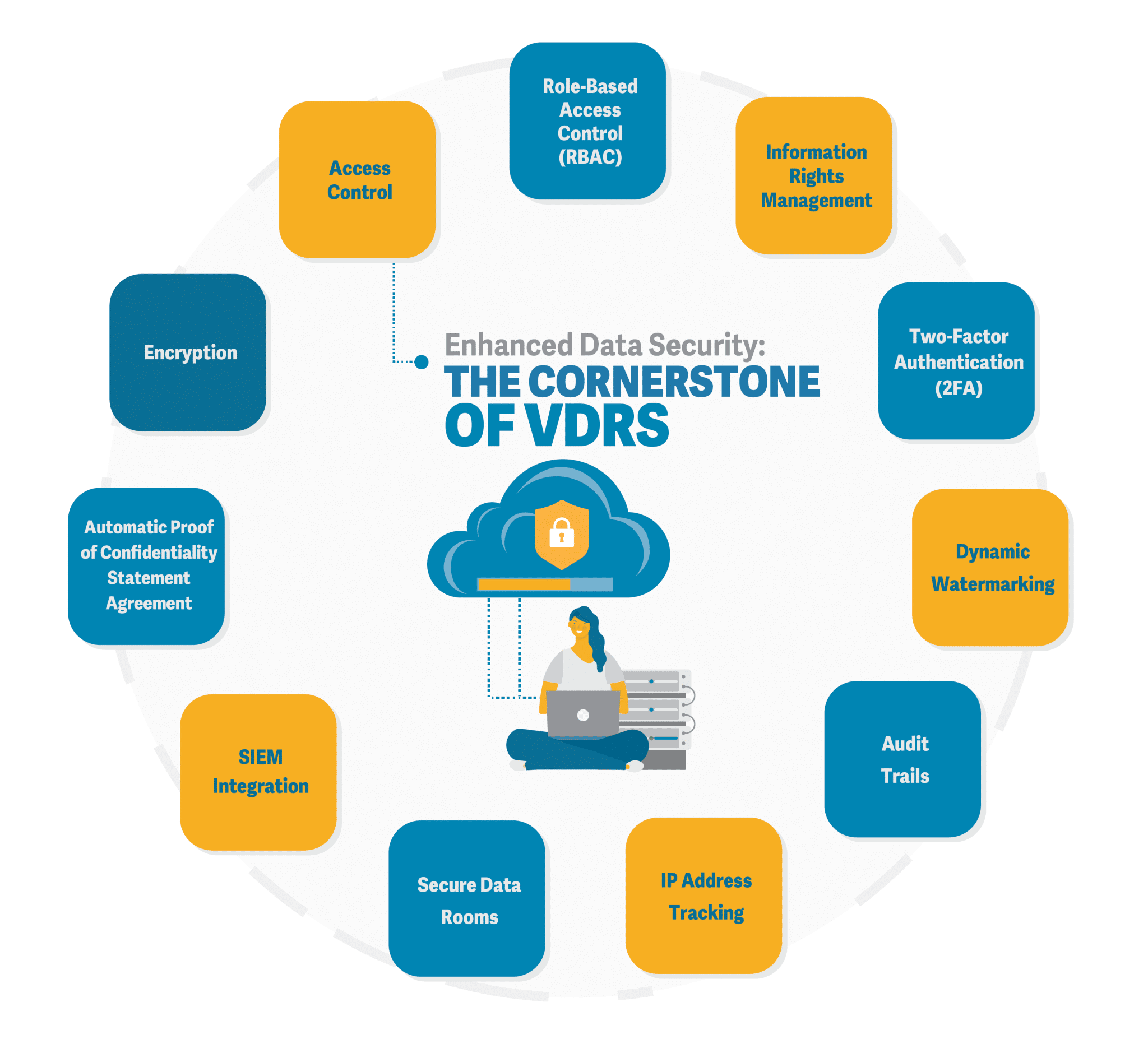
Enhanced Data Security: The Cornerstone of VDRs
Virtual data rooms are designed with a primary focus on data security. They provide a range of security measures that collectively work to safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyber threats. Here are some key security features that contribute to the enhanced data security offered by virtual data rooms:
Encryption: Encryption is a fundamental aspect of data security. VDRs utilize strong encryption protocols to ensure that data is transmitted and stored in an encrypted format. This prevents unauthorized parties from intercepting and deciphering the information, even if they gain access to the data.
AES-256 (Advanced Encryption Standard) is a widely used symmetric encryption algorithm renowned for its robust security and versatility. Employing a 256-bit key length, it ensures a high level of protection against brute-force attacks, making it a favored choice for safeguarding sensitive data. AES-256 operates on fixed-size blocks of data, transforming plaintext into ciphertext through a series of intricate substitution, permutation, and mixing operations.
Its widespread adoption in various domains, including data protection, secure communications, and financial transactions, attests to its reliability and effectiveness in maintaining confidentiality and integrity.
Access Control: VDRs allow administrators to control both who has access to specific documents and folders and also what they are permitted to do with those documents. For instance, lawyers may only be granted access to folders that contain the contracts and legal documents that apply to them and HR staff may only be granted access to folders that pertain to employees and other human resources information. Once those permissions are granted, administrators can then designate the policies that define what actions can be taken with specific documents. For instance, the ability for users to print, save, copy/paste, or take screenshots.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is a security framework used to manage and regulate access to digital resources within organizations. In RBAC, permissions are assigned to roles, and users are then assigned specific roles based on their responsibilities and job functions.
This hierarchical approach streamlines access management by reducing complexity and ensuring least privilege, where users only gain access to the resources necessary for their tasks. RBAC enhances security, as administrators can centrally manage permissions and swiftly revoke or modify access when roles change.
This method minimizes human error, enforces principle of least privilege, and contributes to a more organized and secure digital environment.
Information Rights Management: Information Rights Management (IRM) technology, allows administrators to retain persistent control over documents shared with third parties. Protected documents are AES-256 bit encrypted and can only be opened by users with current rights, so documents can be remotely “shredded”. In other words, a user’s permission to open a document can be revoked retroactively, even for files already downloaded.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): VDRs often incorporate two-factor authentication, requiring users to provide two forms of identification before gaining access. This adds an extra layer of security by confirming the user’s identity through something they know (password) and something they possess (a verification code sent to a trusted device).
Dynamic Watermarking: Some VDRs allow administrators to automatically apply customized, dynamic watermarks to each page of protected documents and spreadsheets, as well as to protected videos.
Watermarks are clearly visible, applied diagonally across the page or screen, yet do not interfere with the readability of the underlying text. The watermark text is customizable, and can have the following dynamic information embedded:
- User’s name and organization
- User’s email address
- User’s IP address
- Current date
- Current time
Watermarks provide a clear indication to the reader that the content is confidential, and since the user’s identity can be included in the watermark, it allows for a simple but effective deterrent against distribution of the printed documents to unauthorized readers.
Audit Trails: VDRs maintain detailed audit trails that record all user activities within the platform. This includes document access, edits, downloads, and other interactions. These trails provide a clear record of who accessed what, adding transparency and accountability to data sharing and can provide administrators with valuable deal intelligence.
IP Address Tracking: Some virtual data rooms give administrators the ability to track the IP addresses of their users with built-in geolocation and organization lookup, so they can see from where their users are logged in as they access the data room.
Secure Data Rooms: VDRs offer the option to create separate data rooms for different projects or transactions. This ensures that only relevant parties have access to specific information, minimizing the risk of unintentional data exposure.
SIEM Integration:Large enterprises implementing security best practices are increasingly requiring integration with a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system to aggregate user activity events, so they have a single source of truth for tracking user activities across all applications. To comply with such requirements, many VDRs can be integrated with a variety of leading SIEM platforms.
Automatic Proof of Confidentiality Statement Agreement: Some VDRs feature clickwrap-compliant logging of each user’s consent to the data room’s confidentiality agreement for applications requiring legal enforceability. VDRs that support the clickwrap standard can bypass manual processes to obtain NDAs, CDAs and LOIs outside of the data room, before inviting a user to the data room, and instead obtain their legally binding consent to the VDRs confidentiality agreement on login.
The clickwrap feature presents the VDRs latest agreement either every time a user logs in, or only when it has changed. Every time the agreement is accepted, the VDR logs the time, IP address and other fingerprint data—all of which makes the log completely defensible in court.
Confidentiality and Collaboration
Virtual data rooms are not only about locking down information; they also promote seamless collaboration while maintaining confidentiality. Here’s how:
Granular Permissions: As mentioned earlier, VDRs allow administrators to set specific permissions for different users. This means that while collaboration is facilitated, individuals only have access to the information they need for their roles.
Real-time Updates: Collaborators can access the latest version of documents in real time, reducing the likelihood of confusion caused by outdated information.
Secure Q&A: Many VDRs provide a secure Q&A feature within the data room that allows users to ask questions and get answers from subject matter experts. This eliminates the need for email communication, which may be less secure and maintains an audit trail of every question posed and its response for the duration of the project.
Time-Limited Access: For temporary collaborators, such as consultants or external auditors, time-limited access to specific documents can be granted. Once the project is complete, their access is automatically revoked. Administrators can also apply expiration dates to documents that have workflow implications, effectively enforcing project deadlines.
Conclusion
In a world where data breaches and cyber threats are on the rise, safeguarding sensitive information is paramount. Virtual data rooms offer a comprehensive solution for businesses and organizations seeking to securely share and collaborate on confidential documents. With encryption, access controls, audit trails, and a range of other security features, VDRs provide a powerful platform for enhancing data security and maintaining the utmost confidentiality in today’s digital business landscape. As technology continues to evolve, virtual data rooms are poised to play an even more critical role in protecting valuable information from unauthorized access and breaches.
ShareVault has been providing secure document sharing solutions to organizations of all types and sizes for over 15 years.